Creating Spatial Data Sources
Creating spatial data sources is done using a wizard. Simply follow the different steps until you reach the end of the wizard. Some user interfaces are common to all data sources and some are specific to each type of data source.
Basic concepts
Including multiple files
In most data sources that read files, multiple files can be integrated together to form continuous maps. It is frequent for CAD users to split the territory in rectangular tiles. By reading all tile files together, JMap administrators can recreate continuous maps. The only prerequisite is that the files contain the same data structure (geometry, layers and attribute types).
File browsing
For selecting files to include in data sources, JMap Admin provides a remote file browser that allows you to navigate the file system of the server where JMap Server is running. In order to select files, these must be located on disks accessible through the server file system and read permissions must be set accordingly.
When browsing the root of the file system, you have the option to create user-defined paths. These paths are shortcuts that can be useful to save time when browsing or can be used to write OS specific paths like Windows UNC (e.g. \\myserver\data).
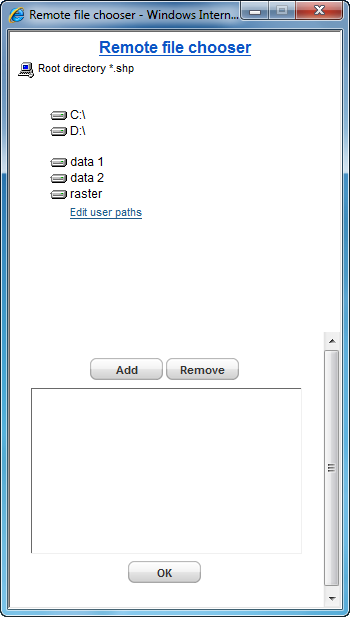
JMap Admin remote file browser with user-defined paths
Creating a new data source
To create a new data source, press the Create button in the Spatial Data Sources list section.
Identification |
|
Name |
Enter a name for the new spatial data source. The name must be unique. |
Description |
Optionally enter a description for the new spatial data source. This description can only be viewed by the JMap administrator. |
Type |
|
Source type |
Select the type of data source that matches the type of the data to read. All supported data source types are presented. |
Note that custom data source types may exist. They are new types of data sources that are developed using JMap SDK for special needs.
The next steps will depend on the data source type you selected. For more information on data source-specific configuration interfaces, refer to the appropriate section by clicking on the links in the following table.
Vector spatial data sources |
|
Spatial data files |
SHP (ESRI), MID/MIF (Mapinfo), GML, DGN, DGNV8, DWG/DXF, CSV, ESRI File Geodatabase, TAB (MapInfo), GPX, KML (Google Maps), VEC (Edigeo), GeoJSON, ADF/E00 (ESRI Arcinfo). |
Spatial data servers |
Database coordinates, Database annotations, Oracle Spatial/Locator, PostGIS, MySQL Spatial, MS SQL Server Spatial, ESRI Geodatabase (personal), ESRI Geodatabase (SDE), WFS Servers, JMap Server, JMap Spatial Table |
Raster spatial data sources |
|
Image files |
GDAL (Geospatial Data Abstraction Library), TIFF/GEOTIFF, ECW/JPG2000 |
Image servers |
|
Attributes
This step applies only to vector data sources.
After the data source-specific configuration section, you need to configure attributes for the data source. All available attributes are listed in a table. By default, all attributes are included but some attributes can be excluded, in which case they will be completely ignored by JMap Server. It is also possible to specify for which attributes JMap Server should create an index for better query response times (this does not affect the map download and display times). These indexes are used when performing attribute queries on these fields. Also, it is possible to look at a sample of the attribute values (10 first values) by clicking on the attribute names.
This section also contains settings to configure external attributes. See External Attributes for more details.
Attributes |
|
Include |
Included attributes are processed by JMap Server. They can be used in reports, to produce thematic maps, for labeling, etc. Excluded attributes are totally ignored by JMap Server. By default, all available attributes are included. |
Indexed |
JMap Server can create an index on an attribute to speed up queries that will use this attribute. If you plan to use an attribute for attribute queries, this attribute should be indexed, especially if the data source has a high number of elements. |
Key attribute |
A key attribute is used when JMap must establish relationships between certain data and your spatial data. It is important to choose an attribute whose values will never change. If you do not need this parameter, you can keep the default value. |
Projections
The projection of the data source must be selected to match the projection of the data. If this is not set correctly, the data display may be invalid. For more information about projection support in JMap, refer to the Geographic Projections section.
Projections |
|
Original projection |
The projection or spatial coordinate system that is used in the data to be read. |
Start update automatically |
This option is a shortcut that launches an update of the data source after pressing Finish in this wizard. When options requiring an update of the data source are modified in the wizard, this option is selected by default. |