Form Designer
The interface of the form designer allows you to define the content and layout of the form.
Forms are organized in a grid, and you can configure the number of rows and columns. Columns and rows can be added to the grid at any moment. All empty rows at the bottom of the form and empty columns at the right of the form will be automatically eliminated when the form is saved.
Each cell of the grid can contain a component of the form (label, text entry field, value list, etc.) but each component can also span several cells horizontally.
Each form can have one or more sections. The user can move from one section to another within a form. This can be especially useful if the form is long or complex.
The following image shows the main parts of the form designer.
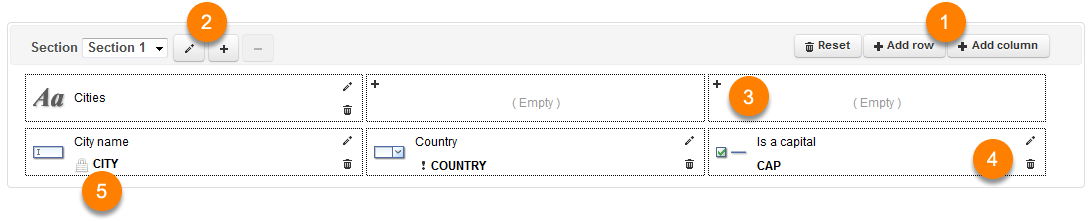
Interface du designer de formulaires
1 |
Click on Add row or Add column to modify the form grid. |
2 |
Click on these buttons to create a new section, to delete an existing section or to rename a section. |
3 |
Click on |
4 |
Click on |
5 |
The |
Most form components must be associated with either an attribute layer, a database field or a search criterion, depending on the type of form created. The Label, Photo, and Group components are exceptions to this rule.
Component settings
Each type of component has its own configuration window. The settings allow you to control the behavior and appearance of the component. The following table describes some of the settings that are common to several components. A comprehensive description of available components is provided further below.
Form component settings |
|
Attribute |
Select the attribute of the layer to which this component is associated. This is the attribute the form component will modify. |
Required |
Determines if this is a required field. The user cannot submit the form until all required fields have been populated. To make a field optional, you must unselect this option. Required fields are identified with a |
Read only |
Select this option to make this a read-only component. The user will not be able to modify the content. This option should be used to modify a component with a default value. |
Column span |
By default, each component occupies only one cell. For a component that spans several cells horizontally, enter the number of cells the component will span. Cells occupied by a spanned component are labeled Spanned. |
Tooltip |
This text is displayed in a tooltip when the user places the mouse pointer on this component. |
Label (prefix) |
Enter static text that will appear above the component. |
Label (suffix) |
Enter static text that will appear at the right of the component. |
Width (pixels) |
Specify the width in pixels of the component entry field, excluding the suffix label. The default value is 100. The width of each column of the form will automatically be the same as the widest component in the form. |
Default value |
Optionally enter a default value to initialize the data entry field. You can use certain functions to initialize the default value of a component. |
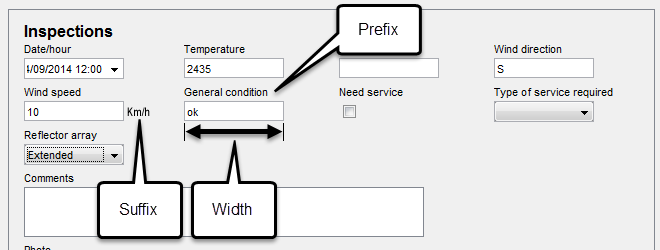
Exemple de disposition des composantes d'un formulaire
The following table describes the various components available to create forms and their specific settings. Note that some components are not available to create attribute queries.
Form components |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Static text to be displayed in the form. The text's alignment (left, right, center) can be specified, along with the font style used to display the text. Certain functions can be used in the label text. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A field used to enter an alphanumeric value. The associated field must be alphanumeric or numeric. Mask formatter: A mask formatter can be used to control the format of the value entered. Multiline: (alphanumeric fields only) If this option is enabled, the entry field will cover several lines of text, making it easier to enter longer text. Max. number of characters: (alphanumeric fields only) Determines the maximum length of the text a user can enter. This must comply with the restrictions of the database field containing the data. Range validation: (numeric fields only) Allows you to define a range of accepted values (e.g. from 0 to 100). |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A list of values from which only one value can be selected. The associated field must be numeric or alphanumeric. The values in the list can be entered manually or be taken from a database: Values Enter the values in the space provided, indicating, for each one, the value to use in the database and the label to display in the list. This value will be used as the data. The label is only used for the information the user will see. If the value and the label are the same, enter the same value twice. Get values from a database You must select the database from which you wish to obtain the values. Afterwards, enter an SQL query that will be executed to obtain the values and labels to be displayed. The order of the fields is important (first the values field, then the labels field). Normally, labels must be unique and sorted. Example: select distinct ID_CITY, CITY from CITIES order by CITY In this example, the ID_CITY field provides the values and the CITY field provides the labels that will appear in the list. Note: At times, labels to be displayed in a list come from a table associated to a data source stored in JMap Server's System database. In such a case, the name of the physical table cannot be known. To solve this problem, you can use this simple approach: instead of entering the name of the table, enter the name of the data source between dollar signs ($). Example: select distinct ID_CITY, CITY from $World cities$ order by CITY |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A value list from which one or more values can be selected. The associated field must be alphanumeric. The value saved in the field is the list of selected options, separated by commas (,). The values in the list can be entered manually or they can come from a database. Refer to List (single choice) for more information. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Populates the associated field for which there are only 2 possible values. The 2 possible values must be specified and be character strings (e.g. true or false) or numerical values (e.g. 0 or 1). If the associated field is boolean, you must use true and false. Checked value: Value to be recorded if the check box is selected. Unchecked value: Value to be recorded if the check box is not selected. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(unavailable for attribute query forms) |
Allows you to select a date. The layer attribute must be of one of the following types: date, datetime or timestamp. This type of component is not available for attribute query forms. Date format: This is the format that the calendar component will use to display the selected date. If the user enters the date manually, he or she must also use this format (e.g. dd/MM/yyyy, yy/MM/dd H:ss, etc.). |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(unavailable for attribute query forms) |
This component allows the user to insert images in a form. In JMap Mobile, it allows the user to take photos with the device's integrated camera. In JMap Pro, the user can select existing images to insert in the form. This component cannot be present more than once in the same form. For a layer attributes form, the photos can be stored in the JMap Server System database (in this case, no configuration is required) or in an external database. When this component is added to a database form, the photos must be stored in an external database. You must then define all required parameters for storing the photos. Storage: Choose the JMap option to store the photos in the JMap database (only available for layer attributes forms) or External to store them in the database of your choice. If you choose External, you must specify the following configuration in its entirety. Database: Select the database where the photos must be stored. This database must be configured beforehand in JMap Admin. Table: Select the table that will contain the information on the photos. This table must have the following structure. The name of the table and fields may vary.
The BLOB field is not required if the photos are stored on the drive and not in the database. Refer to the photo Storage option for more details. Photo ID field: Select the field in the table that will contain the photo's unique numerical identifier. Element ID field: Select the field in the table that will contain the attribute identifying the layer element. This attribute is called the key attribute and it is selected when the spatial data source associated with the layer is created. File name field: Select the field in the table that will contain the name of the file for the photos. Photos persistence: Choose the Database option to save the photos directly in the database, in a BLOB field existing in the table. You must then select the BLOB field. Choose the File system option to save the photos in a folder of the server's file system. You must then enter the path of the folder that will contain the photo files. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
This component displays a value tree structure. The user can select a value in the tree, leaf or branch. The associated field must be alphanumeric. The tree's values can be entered manually or they may come from a database: Values Enter the values in the space below according to the following format:
Get values from a database You must select the database from which you wish to obtain the values. Afterwards, enter an SQL query that will be executed to get the values from a table with a parent-child relationship. An example of a table containing the tree's values:
An example of an SQL query used to read the data and initialize the tree (the order of the fields in the query is important): select parent, child from mytable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(unavailable for attribute query forms) |
Allows you to manage data originating from databases external to JMap and for which a 1 to N relationship exists with the layer elements. Example: Suppose a points layer represents fire hydrants in JMap, and a database external to JMap contains data on the inspections performed on these fire hydrants. For each fire hydrant, 0, 1 or several inspections can be performed. In the layer attributes form of the fire hydrants, the table allows you to display inspection data regarding a fire hydrant, where each line in the table represents an inspection. Depending on the permissions configured, the table can also be used to add, modify or delete the inspection data. The table is always associated with a subform. This subform defines how external data is accessed and how this data can be entered. The subform must be created before the table can be configured. The table parameters allow you to define the external data fields that will be displayed in the table and their order of appearance. Subform: Select an existing subform that will be used to populate the values associated with the table. Fields: Allows you to manage the fields displayed in the table. These are the fields of the subform associated with the table. You can modify the field names, their display order, and their visibility in the table. For more information on using external data with JMap forms, refer to the Database Forms section. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
This component is used to group form components together. A frame with a title will be drawn around the components belonging to the same group. Insert this component in the cell of an empty row to start a new group. This component automatically spans all cells of the row. It cannot be inserted on a row that already has other components. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The following functions can be used to initialize form components.
Functions |
|
username() |
Replaced by the user's code. |
fullname() |
Replaced by the user's full name. |
date() |
Replaced by the current date. |
datetime() |
Replaced by the current date and time. |