Layers can be configured for linear networks (road networks, sidewalk networks, etc.). These will be used for the analyses performed by Tracking. These networks are used to bind the data of mobile units in certain analyses and to produce maps that are easy to interpret.
Networks may or may not be directed. Directed networks increase the reliability of analysis results. In addition, networks can be single or double (one segment for each traffic direction).
1.Open the Network layer section in the configuration of the Tracking extension.
2.Click on Create to create a network layer configuration.
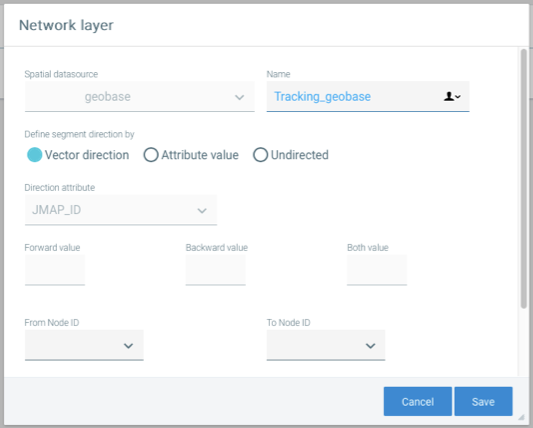
Interface for configuring a road network for analysis
Network layer parameters are described in the following table.
Network properties |
|
Spatial data source |
Each network must be based on a spatial data source configured in JMap Admin. Select the data source. Once the network has been created, you can no longer change this parameter. |
Name |
Name you wish to give the network. |
Define segment direction by |
If the network has a direction, you must tell Tracking how to interpret the direction. In some analyses, Tracking will make better decisions if the network is directed. Vector direction: Tracking uses the vector direction (digitizing direction) to know the direction of network segments. This works well if the network is doubled (one segment per traffic direction). Attribute value: Tracking uses the value of an attribute combined with the vector direction (digitizing direction) to know the direction of the network segments. The values of the attribute used indicate the relationship between the vector direction and the traffic direction. This works well with single or double networks. Undirected: The network is undirected and Tracking will ignore traffic directions during its analyses. |
Direction attribute |
If you selected the Attribute value option, you must select the attribute containing the values that must be used to interpret the traffic directions. |
Forward value |
If you selected the Attribute value option, enter the attribute value indicating that the traffic direction is the same as the vector direction. |
Backward value |
If you selected the Attribute value option, enter the attribute value indicating that the traffic direction is contrary to the vector direction. |
Both value |
If you selected the Attribute value option, enter the attribute value indicating that the traffic is in both directions, with no connection to the vector direction. |
From Node ID |
If your network data contains topology, you can indicate the attribute containing the identifier of the node from which the segments originate. Using a network with topology improves the results of certain analyses. |
To Node ID |
If your network data contains topology, you can indicate the attribute containing the identifier of the destination node for the segments. |
One Way |
Select the attribute that indicates if the network segment is a one way. Some network data sources (not doubled) use such an attribute. If the value is 1 or true, it is a one way that matches the direction of the vector. Otherwise, it is not a one way. |
Street Name |
Select the attribute containing the street name of the network segments. Tracking uses this information to record the streets where the mobile units have traveled. If this is not applicable, do not select anything. |
Unique ID |
Select the attribute containing the unique identifier of the network segments. Tracking uses this information to record the streets where the mobile units have traveled. If this is not applicable, do not select anything. |