Basic Concepts
This JMap extension adds edition tools to a JMap Pro application. These tools allow you to add and modify elements and their attributes on editable layers. They also allow you to perform geometrical operations on the elements of all layers (calculating intersections, unions, buffers, etc.).
Only one layer can be edited at a time. All edition operations are performed on that layer. To edit another layer, this layer must be selected beforehand. Edition tools function differently, depending on the layer’s characteristics.
Edition operations on the Annotations layer
This layer exists in every JMap project. It is the default editable layer. It offers unrestricted edition functionality by allowing you to mix different types and styles of elements. It does not have any attributes (descriptive data), therefore it is impossible to add attribute data to elements that are drawn.
Edition operations performed on this layer are not persistent, meaning they will be lost when the session terminates if they are not exported. To save this data, two options are possible: creating a context with an option to save annotations or exporting towards a file (shp, mid/mif, kml or wkt) on the local workstation using the JMap Exportation extension. In the first case, the edited elements will become available again when the context is opened. In the second case, the data file can be reopened using the JMap Importation extension.
Edition operations on the Annotations layer can be useful to create rough sketches and annotations in a simple and less restrictive way.
Edition operations on an editable layer
Editable layers allow you to edit data, which includes adding, moving, modifying and deleting geometries as well as entering or modifying their attribute values. The JMap administrator can grant a user the permission to modify the contents of one or more layers within a project. In addition, a user can create personal layers directly in the Pro application if the JMap administrator grants that user permission to do so, and the administrator can also grant other users permissions to edit those layers. In both cases, editing data is done in a similar way.
Editable layers are more structured than the Annotations layer. Each one has a unique element type and other types of elements cannot be added. They also have a defined set of attributes, which will be present on each element of the layer. Lastly, an editable layer has one or more styles (depending on the scale) that will be applied to all of the layer’s elements.
Performing edition operations on an editable layer is subject to the layer’s particularities. For instance, any drawing tools for element types that are incompatible with the layer will be deactivated. Interfaces to modify the style of incompatible elements will also be deactivated.
Entering the attributes of new elements is done using a form that displays when each element is added. You can enter attribute values on this form. In editable layers offered by the JMap administrator, some attributes are required and others are optional. The form can only be closed once all required attributes have been populated. In personal layers, all form attributes are optional.
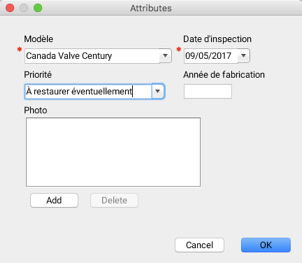
It is also possible to open the attribute entry form by right-clicking on a map element.
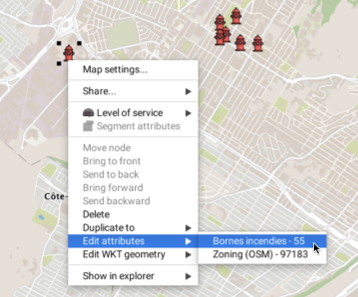
Editing attribute data can also be done using the layer’s elements explorer. To begin editing attributes, you must first enable attribute data edition in the explorer by clicking on the  icon and then clicking in the cell containing the data to modify.
icon and then clicking in the cell containing the data to modify.
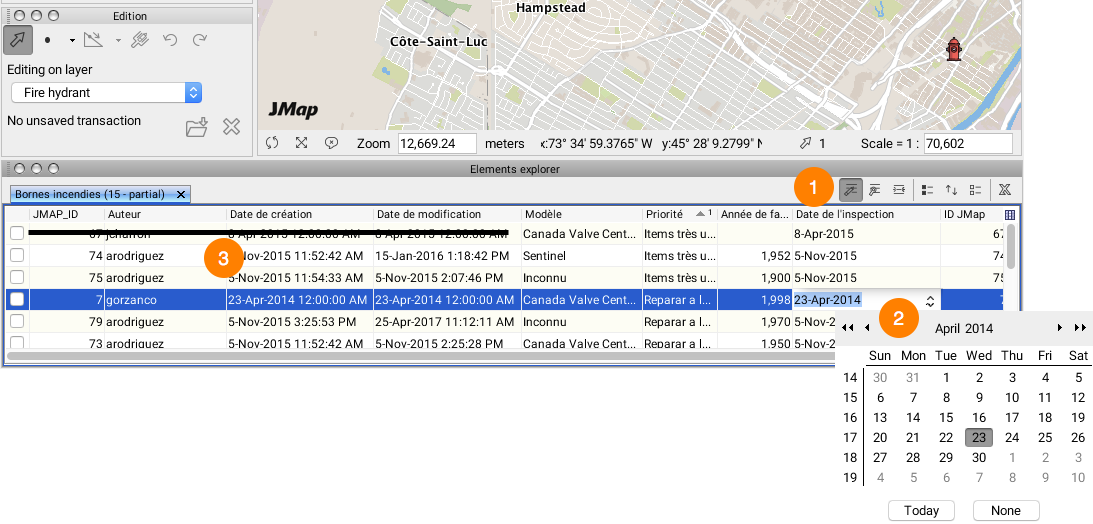
| 1 | Enabling the  icon allows you to modify the cells. icon allows you to modify the cells. |
| 2 | Click in an editable cell to enter the new attribute value. Some cells have their own entry interfaces (a calendar for a date attribute, for instance). Validation rules on the type of data entered will be applied after the data is entered. |
| 3 | Some system attributes cannot be modified. These attributes are automatically populated by JMap and used for management purposes. |