Performing Spatial Operations
Table of contents
The Edition extension offers two types of spatial operations: geoprocessing and spatial tools.
Geoprocessing concerns the set or a selection of the elements of the involved layers and their result is a set of new geometries added to the Annotations layer.
The operations performed by the Spatial Tools concern the elements selected beforehand and their result is one or more new geometries that are added to the Annotations layer.
The layers attributes are not retained in the results. The elements resulting from the operations can be selected and copied into other layers using the Edition tools and the context menu.
When you perform spatial operations on editable layers, you can hold down the CTRL key to retain only the result of the operation, that is, by automatically deleting the editable elements that were selected.
Geoprocessing
Intersection
You can intersect the whole or a selection of the elements of two layers:
-
Select the Intersection function from Tools -> Geoprocessing in the menu bar.
-
From the drop-down menus, select the layers whose elements will be intersected and press Execute. The resulting elements of the intersection appear colored and are added to the Annotations layer.
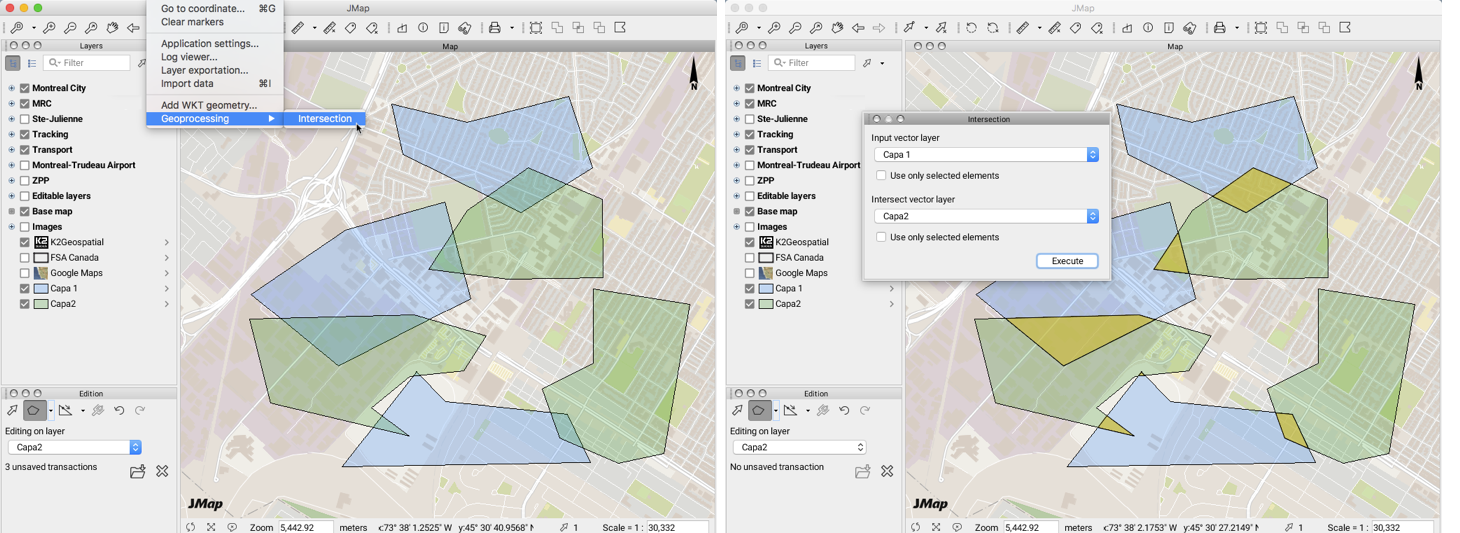
-
You can then copy them to another layer displayed in the application if you have permissions to add elements to it.
Spatial tools
Spatial operations are performed on one or more selected elements. A spatial operation results in a new geometry added to the Annotationslayer.
When you perform spatial operations on editable elements, you can press and hold down the CTRL key to keep only the results of the operation, i.e. automatically deleting the editable elements that were selected.
 Buffer
Buffer
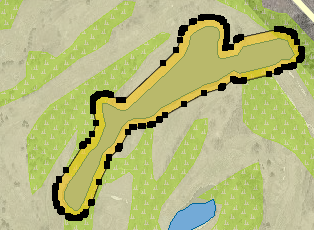
Creates a buffer zone around the selected map elements. Select the desired elements and press this button. You must then specify the size of the buffer, i.e. the maximum distance between any point of the buffer and the selected elements. The size can be negative, in which case the buffer can be smaller than the selected elements. The size of the buffer is indicated in the map’s unit of distance.
The figure shows a 10 m buffer around a lake.
 Union
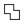
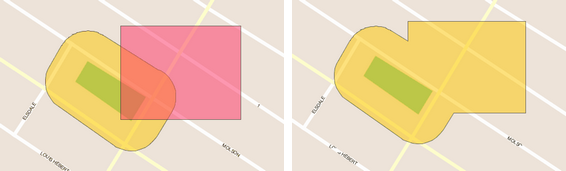
Union
Creates a new element by uniting the selected elements. Select at least 2 elements.
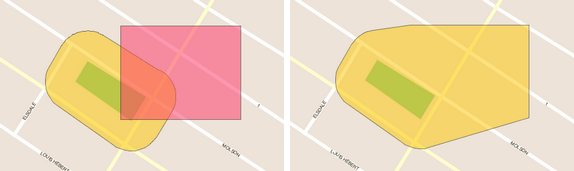
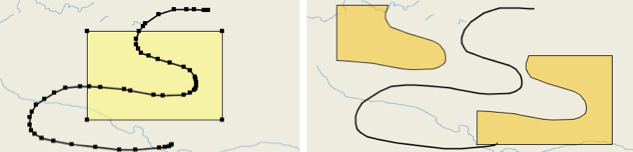
 Intersection
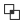
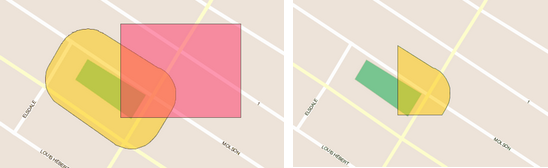
Intersection
Creates a new element that is the intersection of the selected elements. Select at least 2 elements.
 Difference
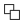
Difference
Creates a new map element that is the difference between the first selected element and the others. In other words, all elements are subtracted from the element that was selected first. Select at least 2 elements.
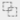 Elementary polygons
Elementary polygons
Creates new elements resulting from the intersection of two polygons.
 Split polygon
Split polygon
Creates new elements resulting from the splitting of a polygon using a line. Select a polygon and a line that come from two different layers.
 Convex
Convex
Creates a new element that is the smallest convex polygon that entirely covers the selected elements.